WORKS OF ALBERT EINSTEIN
- The first of his articles of 1905 was titled “A heuristic point of view on the production and transformation of light”.
- The fourth in degree of importance, is closely related, with the article on molecular theory. It is a very elaborate piece of statistical mechanics.
- On the motion required by the molecular kinetic theory of the heat of small particles suspended in a stationary liquid, covered his studies on Brownian. motion.
- "On the electrodynamics of moving bodies"). In this article Einstein introduced the theory of special relativity by studying the movement of bodies and electromagnetism in the absence of the force of gravitational interaction.
Albert Einstein a Nobel laureate and probably the world’s greatest theoretical physicist ever played a significant role in revolutionizing the understanding of Physics all over the world.
Among Albert Einstein's best works are:
Theory of relativity and E = mc²

Albert Einstein is known all over the world for the famous equation – E = mc². One may not really know what the theory actually is but the fact that it was Einstein behind it is recognized universally. He published a paper “Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper” i.e, ‘On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies’ in September 1905. It brings together Maxwell’s equations for both electricity and magnetism with the world of Quantum Mechanics. This theory explained in the paper was later christened as Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity. He was the one who developed both the special and general theories of Relativity. It wasn’t accepted with ease and was rather contentious for several years before being accepted by the scientific fraternity.
Quantized atomic vibrations

Albert Einstein proposed the Einstein Solid Model where if each atom is a lattice in an independent 3D quantum harmonic oscillator and all atoms oscillate with the same frequency; each atom oscillated independently. This model showed that Quantum Mechanics could actually solve the specific heat in Classical Mechanics. It was proposed by Albert Einstein in the year 1907 using the Planck’s quantization assumption.
Wormholes

It is a concept which is depicted by Einstein-Rosen Bridge way back in 1935. Wormhole, in physics, is a hypothetical feature of space and time continuum that is a path through the continuum itself. Though there are no practical proofs for the same; in spite of this ample evidence exists theoretically to validate the conjecture of their existence. It is a derivative of Einstein’s theory of relativity and basically is a space-time curvature which joins two different and far-off times or places.
Unified field theory
Einstein illustrated the ‘Unified Field Theory’ in his paper ‘On the Generalized Theory of Gravitation’ in the year 1950. It was his vision to unify gravity with other laws of Physics and hence the endeavor towards this theory. He worked through most of the latter part of his career on this but his efforts were unsuccessful. He was so deeply engrossed in it that other significant advances and events in mainstream physics were ignored by him. Basically the Unified Field Theory was a series of experiments conducted by him to accommodate electromagnetism in his geometric theory of gravitation.
Adiabatic principle and action-angle variables
The 1910s was a decade when a lot of transformation and discoveries unfolded in the field of Quantum Mechanics. The principles of Quantum Mechanics developed by Einstein formed the basis of Neils Bohr’s explanation of the motion of electrons in atoms and the periodic table of the elements. Einstein showed in 1911 that the adiabatic principle orchestrated by Wilhelm Wien showed that the quantity that has been quantized in a mechanical motion must be an adiabatic variant.
General relativity and the Equivalence Principle
The tool of modern Astrophysics; General Relativity is a Gravitational Theory that was developed by Albert Einstein in the years between 1907 and 1915. The observed gravitational attraction between masses is a result of the warping of space and time by those masses. This theory forms the basis of the present perception of Black Hole. Einstein published an article in the year 1908 where he explained the Equivalence Principle which says that the rules of special relativity applies for a free falling observer as free fall is an inertial motion. In accurate scientific terms as put forth by Albert Einstein Equivalence principle states that the weak equivalence principle holds, and that ‘The outcome of any local non-gravitational experiment in a freely falling laboratory is independent of the velocity of the laboratory and its location in spacetime.’
Schrödinger gas model
The man behind Schrödinger gas model was not only Schrödinger himself but Albert Einstein too. However the latter declined a request from Schrödinger to have his name included as co-author for the paper. Albert Einstein suggested Schrödinger to treat energy levels of a gas as a whole instead of treating them as individual molecules; an extension of the application of Planck’s idea. Using Einstein’s idea, Schrödinger derived the thermodynamic properties of a semi classical ideal gas using the Boltzmann distribution in a paper.
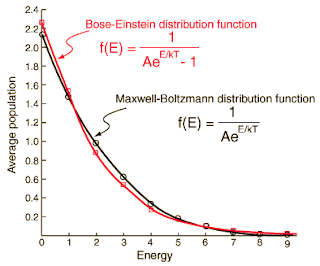
Bose–Einstein statistics
Commonly known as B-E statistics; it is a property in Quantum Statistics which illustrates one of the ways of how a collection of indistinguishable particles may occupy a set of available discrete energy states. These very statistics are used in present day to describe the behavior of a collection of bosons. In 1924 Satyendra Nath Bose presented to Einstein a statistical model which was translated and submitted by the latter. The Bose-Einstein Condensate phenomenon was also derived around that time. The Bose-Einstein statistics apply only to particles that do not follow Pauli Exclusion Principle.
Wave–particle duality:
All particles exhibit both wave and particle properties is what is stated by Wave Particle Duality. An important concept of Quantum Mechanics; this is a paradox and is often described as a basic Universal property. Albert Einstein presented a paper in 1909 where he first provided explanation for the Wave-particle duality. Infact the photon concept was derived out of this paper. Einstein postulated that electrons can receive energy from electromagnetic field only in discrete portions.
Photons and energy quanta:
Albert Einstein proposed that light consists of localized particles in a paper in the year 1905.This idea was rejected by scientists all round the fraternity including Planck and Neils Bohr and it wasn’t until the year 1919 that it was actually accepted after Robert Millikan’s detailed experiments. It was concluded by Albert Einstein that each wave of frequency f is associated with a collection of photons with energy hf each, where h is Planck’s constant. This went on to explain the Photoelectric effect and several experimental results. It was for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect that Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.